Electomagnetic Thrusters
The presently known spacecraft propulsion methods:
The present known spacecraft propulsion methods use Magneto-Plasma-Dynamic Thrusters (MPDT) to generate thrust. This system ionizes gaseous materials and feeds them into an acceleration chamber, where magnetic and electric fields are created using a power source. The particles are then propelled by the Lorentz force. Unlike chemical propulsion, this method does not rely on fuel combustion, making it more efficient for driving spacecraft with electrical power.
Yet the MPD thruster technology has been of no commercial interest due to several problems, such as interplanetary spacecraft power systems such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators and solar arrays being incapable of producing that much power. Also, limitations are encountered due to restrictions on the temperatures that can be sustained by engine components. These electric thrusters propel the spacecraft using the same basic principle as chemical rockets—accelerating a mass in the form of energetic charged particles and ejecting it from the vehicle.
Also, there are propulsion systems that use a combination of strong and weak electromagnets to repel each other and move outer-space crafts or loads. In addition, there are inertial propulsion devices that consist of rotational motors that turn a transmission and move an inertial mass in an oscillating motion.
Some aerospace propulsion technologies are based on the applications of the reaction principle, creating motion by expelling propellant mass from a vehicle.
The new propulsion system introduced in this text uses an electromagnetic thruster that can be powered by electricity instead of using chemical fuels that emit exhaust.
In this method, propulsion is generated by any combination of pushing or pulling to modify the translational motion of a combination of objects.
One great advantage of the present electromagnetic thruster is that it doesn’t require a reactive base or medium to produce repelling force.
Still another advantage is that it doesnot let external material across propellers preventing exposure to damage the components. The energy needed for propulsion may come from an external link like from the storage of onboard batteries or the environment like solar radiation.
In this text, we are introducing a new mobile power source capable of moving on roads, water, sky, and in the outer space.
I was truly amazed by what I witnessed. In the field of transportation, electromagnetic thrusters are destined to be the transformative innovation we've long envisioned. Capable of operating on roads, off-road, on water, in the sky, and even in the vastness of outer space, they are set to revolutionize our travel experiences. By tapping into electrical power, they create unmatched thrust and move payloads with incredible ease, making them far superior to any other propulsion technology. Electromagnetic thrusters are not just the future; they are the key to unlocking a new era in propulsion systems. Let's embrace this electrifying journey ahead!
This Electromagnetic propulsion system constitutes at least an identical pair of reciprocating linear motors performing a back-and-forth cycle, each mounted on a rotary motor running on half-circle steps. Each linear motor with a rotary motor is termed as a module in the proceeding description.
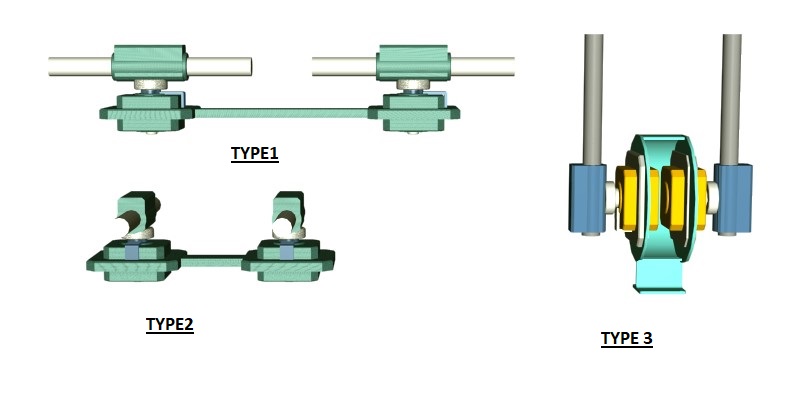
The linear motors of said two modules are mounted and secured at mid portions of their stator arms on said rotary motor armatures, lateral to axes of rotation of the associated rotary motor armature.
The two modules are placed apart and secured to the vehicle in a mirror position to each other. When power is supplied, two linear motor armatures move in a cycle along associated stator arms and rotate with accompanied rotary motor armatures in opposite directions to each other in unison during each rotation of rotary motors, performing a cycle of back-and-forth action. Thus the said two modules with the reciprocating linear motor pairs carrying rotary motors driven in opposed directions operate in identical specifications.
The electricity power supply and connections to controls of linear motors are carried over the housing of the rotary motor and connected to the terminals of the supply source.
Propulsion requires a force to cause motion with a second system being pushed backwards. This second system to be pushed backward is producing on stator by the armature.The linear motors are used in combination with rotary motors, considering the mechanical aspects of the system, including the mass of the moving parts, the speed of their movement, and the distance over which the force is applied. In the context of propulsion, the force generated by the system would be used to propel a vehicle.
The linear motors of said two modules are mounted and secured at mid portions of their stator arms on said rotary motor armatures, lateral to axes of rotation of the associated rotary motor armature.
The two modules are placed apart and secured to the vehicle in a mirror position to each other. When power is supplied, two linear motor armatures move in a cycle along associated stator arms and rotate with accompanied rotary motor armatures in opposite directions to each other in unison during each rotation of rotary motors, performing a cycle of back-and-forth action. Thus the said two modules with the reciprocating linear motor pairs carrying rotary motors driven in opposed directions operate in identical specifications.
Propulsion requires a force to cause motion with a second system being pushed backwards. This second system to be pushed backward is producing on stator by the armature.The vehicle-attached electromagnetic thruster can move about anywhere without the support of the medium through which it travels.
The electricity power supply and connections to controls of linear motors are carried over the housing of the rotary motor and connected to the terminals of the supply source.
Importance of EMT :
The force applied when driving a vehicle is not just important; it's fundamental to mobility as we know it. Traditional internal combustion engines harness thermal pressure on the piston head from expanding gases, translating that force into the momentum that drives us forward.
Meanwhile, jet and rocket engines take a different approach, generating thrust through a reactive force created by expanding gases at the exhaust nozzle. However, this method has limitations, as the expelled gases cannot be recycled for further use.Now, imagine a groundbreaking shift in technology: the rise of advanced electromagnetic thrusters. Unlike traditional engines, these thrusters employ a magnetic rod to create a powerful reactive force that acts directly on the vehicle. This innovative system can sustain propulsion indefinitely, as long as the vehicle requires it.
The advantages of this technology are undeniable. A solid metal rod can generate a much greater reactive force than conventional engines' non-recyclable gas emissions. This remarkable advancement ushers in a future filled with "vehicles powered by electromagnetic energy," setting the stage for a revolutionary transformation in efficient and sustainable transportation. Embracing this innovation could fundamentally change our perspective on mobility, leading us into an extraordinary new era of travel. Let's seize this opportunity to redefine how we move within our world.
Theory based on new electomagnetic thruster :
When current flows through a conductor, an electromagnetic field is created to generate a force known as a Lorentz force, the conductor to push in the direction perpendicular to the conductor and the magnetic field. This force is used to propel the desired object or particles.The force generated by electromagnetic propulsion system involves the interaction between the electric currents and magnetic fields within the system. The force can be calculated using the Lorentz force equation, given by: F=q (E+v.B)
where:( F ) is the force (in newtons),( q ) is the electric charge (in coulombs),( E ) is the electric field (in volts per meter),( v ) is the velocity of the charge (in meters per second),and ( B ) is the magnetic field (in teslas) - which is the sum of an electric force and magnetic force .The Biot-Savart law allows to determine the magnetic field at some position in space due to an electric current.
If we have a coil with Inner Diameter R: Diameter of the ferrous core.
Outer Diameter of Coil (R1): Outer diameter of the electromagnetic coil.
and let the Length of Coil (L): Length of the coil.
Let the Current (I): flow through the coil within voltage (V): applied to the coil.Then the magnetic field ( B ) inside a solenoid (long coil) can be
approximated using the formula:
where:
(μ0 ) is the permeability of free space
( N ) is the number of turns of the coil.
(I) is the current through the coil.
(L) is the length of the coil.
Force on the Ferrous Core will bewhere:
(μ0 ) is the permeability of free space
( N ) is the number of turns of the coil.
(I) is the current through the coil.
(L) is the length of the coil.Force on the Ferrous Core:
The force (F) on the ferrous core can be derived from the
magnetic pressure acting on the core. The magnetic pressure (P)
is given by:------1
The force (F) can then be calculated by multiplying the magnetic
pressure by the cross-sectional area ( A ) of the core----2
For a core with diameter (R):
------3
combining therse equations we get
-------4
Substituting B in to force :
---------5
The force acting on the ferrous core is:
-----6
This solenoid is ideal and uniform in the magnetic field.
More details are available at down load Electromagnetic Thrusters
Patent App :LK/P/1/22948- Sri lanka
We are looking for an entrepreneur or investor to commercialize this product. Please contact at leel6391@yahoo.com
<<<<Previous-----||-----Next >>>

This work is licensed under a Creative
Commons Attribution-NoDerivs 3.0 Unported License.
For more details Contact : Leelananda Jayasuriya
E-mail : leel6391@yahool.com
Search Engine Submission - AddMe
Style Social Media Buttons
